Salt Toxicity in Broilers
By Gabriel Senties-Cue, MS, MVZ, DACPV
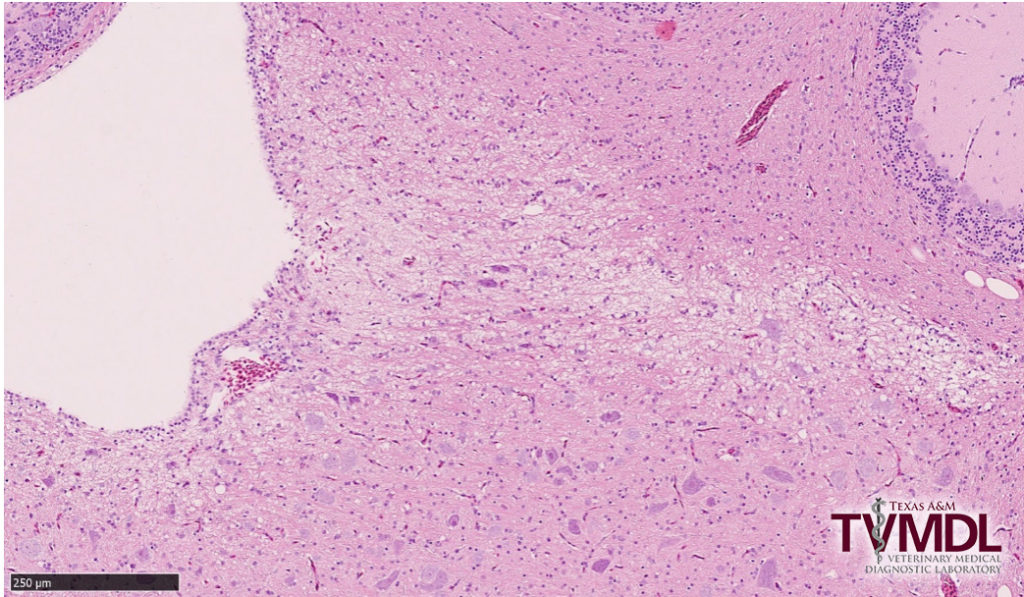
Salt toxicity was recently diagnosed in a 17-day-old, meat type chicken flock. Twelve birds were submitted to the Texas A&M Veterinary Medical Diagnostic Laboratory (TVMDL) in Center. Clinical history noted increased mortality starting at 2-weeks-old. At necropsy examination, all the birds had an edematous brain with poorly defined cerebellar folia and cerebrum lobes, thin blood, and darkened livers; one bird had moderate accumulation of a clear, gelatinous material in the subcutaneous tissue of the abdominal area. Histologically, there were areas of vacuolation in the cerebellar white matter and cerebrum (see Fig. 1). Toxicology analysis on five brain samples revealed high levels of sodium in all of them, with a range from 8,810 ppm to 14,300 ppm. Sodium levels above 7,600 ppm in the brain of chickens are considered toxic.
For more information on this case, contact Center Resident Director Dr. Senties-Cue. To learn more about TVMDL’s test offerings, visit tvmdl.tamu.edu or call 1.888.646.5623.